Achievements
- Development of Panchgavya Products
A Research Centre for the development and production of Panchgavya products obtained from indigenous cow urine and cow dung has been established. Four Panchgavya Production and Testing Units viz. Gobar Gamla Unit, Cow Urine Distillation Unit, Mosquito coil Manufacturing Unit and Ghanvati Manufacturing Unit have been established. Pilot production of various Panchgavya products like Gobar Gamla, Cow dung Havan Tikiya, Cow Urine Distillate, Herbal Mosquito Coil and; Herbal wound Healerointment, Anthelmintic and Hepatoprotective Ghanvati tablets have been initiated for standardization, scientific validation and production.


Panchgavya Products Gobar Gamla
Panchgavya Products Cow Urine


Panchgavya Products Havan Tikiya
Panchgavya Products Mosquito Coil
- Modified Handmade Cloning Technology (mHMC) for oocyte enuleation and electrofusion of embryo
The handmade cloning technology was simplified by innovation of indigenously designed cost effective microtool for enucleation of in vitro matured oocytes under micromanipulator. Instead of using expensive disposable microsurgical blade under stereomicroscope, an indigenously designed and cost effective bisection blades and aspiration pipettes for aspiration and instant discard of one halve of matured oocytes have been developed. These microtool can be used for mass production of high producing cows and bulls by cloning technology. These microtool can also be used in human IVF laboratories for splitting of 2-cell embryos for the purpose of embryo cloning.
- Bioclimatograph Technology
University has developed Bioclimatograph for different districts of Madhya Pradesh which help in forecasting various parasitic diseases of animals. Based on the temperature, rainfall and relative humidity of each district, the incidence of the gastro intestinal nematodosis in the particular geographical area is forecasted well in advance so that prophylactic and curative strategies can be planned in advance. The information regarding the onset of these diseases is conveyed to the farmers of respective areas so that they may get ready and arrange the required prophylactic measures. This technique may be useful tool in enhancing the farmers’ income by reducing the losses due to disease sufferings, use of anthelmintic and thereby reducing the cost of production. The university has developed bioclimatographs for 38 different districts of Madhya Pradesh.
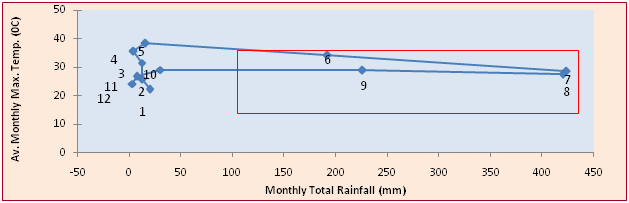
Bioclimatograph for Different Districts of Madhya Pradesh
- Monitoring of water toxicants in water-bodies of Madhya Pradesh
Field survey of target areas for heavy metal water contaminants in and around Jabalpur and Amarkantak was undertaken. The surveillance study was made on the basis of questionnaire (Passive Surveillance) and personal Interview of community living around these target area and their problems by using water resources (Active Surveillance). The investigation revealed that concentration of Lead in 17 water bodies out of 29 water bodies of Narmada River was found above the Maximum Permissible Limit. The concentration of Cadmium was found above the Maximum Permissible Limit in 3 water bodies out of 29 water bodies. The concentration of Copper and Zinc was found below detectable limit in all 29 water bodies undertaken for the study.
- Anaemia chart
University has developed anaemia chart which shows the images of eye of goat of different level of anaemia and their corresponding level of infection. This chart is used to measure the level of anaemia of infected goat by matching their eye colour. By using this chart lightly infected animals are segregated from the heavily infected animals of particular herd. So the treatments are given to only those animals that really needed instead of treating all animals of the heard thereby reducing the cost of anthelmintic and also can prevent development of anthelmintic resistance. So, along with bioclimatograph, this tool is also useful in enhancing the farmers’ income by reducing the cost of production.
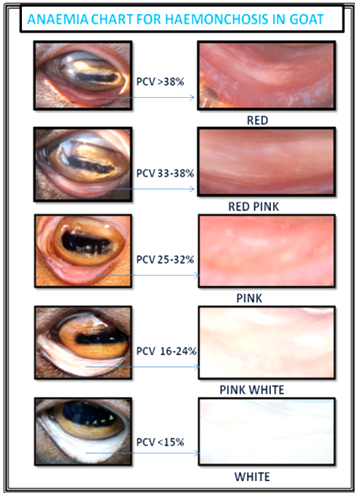
Developed Anaemia Chart
- “Myostatin Gene Knocked-down Goat” to enhance meat production
A novel micromanipulator based “modified handmade cloning” (mHMC) has been developed which significantly enhances the success rate and speed of removal of nuclei from oocytes. Compact SCNT morula using reprogrammed cumulus/fibroblast cell line was produced with ovi-ductal co-culture. Human and mouse cooks culture (RVCL and Blast media) with certain modifications for developing SCNT embryos was used. Normal SCNT embryos were surgically transferred in synchronized recipients which showed that 70 to 80 SCNT embryos were transferred successfully in 15 synchronized goats.
- Herbal Aushidhi Vatika
University has developed aushidhi vatika (herbal garden) at Amanala Farm in collaboration with Ayurvet Limited, New Delhi. Twenty two medicinal herbs have been cultivated in 5 Acre of land. A potential medicinal herb, Mucuna pruriens (Kaunch) has been produced which is used for treating Parkinson disease. Other medicinal plants namely Kalmegh, Brahmi, Ashwagandha, Punernava, Amaltas, Aloe vera, Giloy, Neem etc. have also been cultivated. All produce are sold to Ayurvet Limited in view of resource generation for the University.


Herbal Aushidhi Vatika
Herbal Aushidhi Vatika
- Development of species specific PCR primers for identification of Indian wild pig
Indian Wild pig (Sus scrofa cristatus) is a protected species under the 3rd schedule of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, which is extensively poached for meat. The species specific primer pair has been developed to differentiate Indian wild pig from domestic pigs and other pig races of the world using the amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS). The species specific primer pair can be applied for forensic investigation to differentiate the meat samples of domestic and wild pigs.
- Composition of strategic Azolla as protein supplement
In the diet of non-descript cows, mustard oil cake (MOC) as a conventional protein source was successfully replaced by Azolla meal as unconventional protein source. Azolla meal supplementation lowered the cost of milk production and also improved the health status of non-descript cattle

Azolla
- Development of prosthetic Limb for cattle
University has developed Prosthetic Limb (Artificial Limb) which is made of up poly-propylene fibre. The prosthetic limb may be used as rehabilitation tool for cattle which is fixed after amputation of fore or hind limb. Prosthetic materials are used to replace an absent or missing limb or making an artificial limb as per the contour of normal limb. Characterized by distance osteogenesis, the implant is not rejected from the tissue but it is surrounded by a fibrous connective tissue viz. gold, cobalt-chromium alloys stainless steel, polyethylene and polymethylmethacrylate. It is of three types; Bio-tolerant, Bio-inert and Bio-reactive.

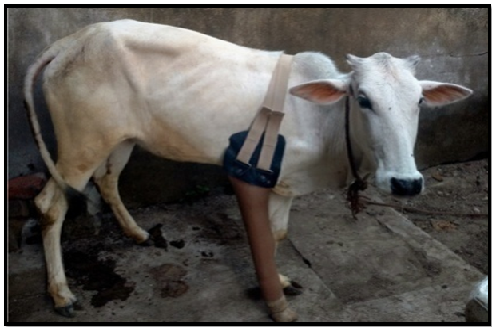
Artificial Limb
Cattle fixed of Artificial Limb
- Development of Commercial Dual Purpose Colour Bird “Narmada Nidhi” with strains of 25% Kadaknath and 75% JBP Colour
A multicoloured dual purpose coloured bird has been developed by crossing and backcrossing of Kadaknath and Jabalpur Colour population. Birds mature at 162 days of age and produce more than 220 eggs in intensive, 191 eggs in semi intensive and 173 eggs annually in free range system. Birds are very popular among farmers and have greater demand in rural backyard poultry for both table and egg production purposes. The new variety of bird “Narmada Nidhi” has been recognized by ICAR, New Delhi.

Narmada Nidhi
- Establishment of Nucleus herd of Sirohi and Barbari goats at Amanala Farm for distribution of superior germplasm
Male and female goats of Sirohi and Barbari breeds were procured from their respective breeding tracts and from Central Institute for Research on Goats (CIRG) Makhdoom, Farah, Mathura. Attempts have been made to develop nucleus herds of Sirohi and Barbari breeds by randomly allotted goat population to superior germplasm buck of each breed so as to develop respective nucleus herds with superior genetic base.

Sirohi and Barbari Goats at Amanala Farm
- Development of designer egg
Dietary supplementation of Nigella sativa, Withania somnifera, Selenium and Vitamin E produced enrichment of egg with increased concentrations of SELENIUM to 28.65 per cent and Vitamin E to 30.35 per cent and also reduced 15 per cent of cholesterol in comparison to normal egg.
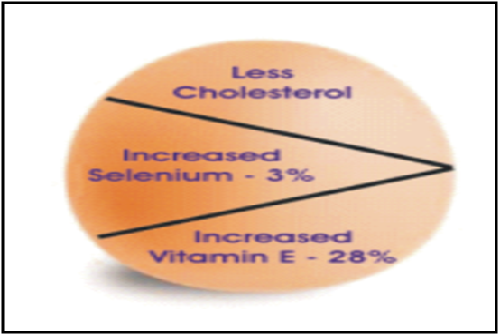
Designer egg
- Prevalence study on Gastro Intestinal Parasitism in livestock
Bioclimatograph of different Agroclimatic zones of Madhya Pradesh has been developed for prediction of infection of Haemonchus contortus, Trichostrongylus sp and Oesophagostomum species of nematode infection. District wise mapping of GI parasites has also been done in various agroclimatic zones of Madhya Pradesh. On the basis of epidemiological data it is estimated that prevalence as well as intensity of Strongyle infection was high in the monsoon season in the month of July to October and was least in the winter season. Predominant Strongyle was the Haemonchus sp which was ranging about 70-80 per cent.
- Development of Myostatin Gene knocked down goat to enhance meat production
A novel micromanipulator based “modified handmade cloning” (mHMC), which significantly enhances the success rate and speed of removal of nuclei from oocytes, has been developed. Compact SCNT morula reprogrammed cumulus/fibroblast cell line were produced using mSOF with oviductal co-culture. Successfully used human and mouse COOK culture (RVCL and Blast media) media with certain modification for developing SCNT embryos. Normal SCNT embryos were surgically transferred through laparoscopies aided embryos transfer technology in synchronized recipients.
PATENT GRANTED (2017-18)
- Development of cost effective microtool for oocyte enucleation during SCNT embryo production.
Patent No.: 297821
PATENT FILED (2017-18)
- Development of a “Rapid strip based test for identification of adulteration in Milk”.
Patent Application No: 201821008795 - Development of Species Specific PCR Primers for Identification of India Wild Pig.
Patent Application No: 43/MUM/2015A
SCIENTIFIC LINKAGES
- Rastriya Krishi Vikas Yojna (RKVY), Bhopal (M.P.)
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi
- Madhya Pradesh State Agricultural Marketing Board (MANDI), Bhopal (M.P.)
- Madhya Pradesh Council of Science & Technology, Bhopal, (M.P.)
- MP Biotechnology Council, Bhopal (M.P.)
- Ministry of Forest, Govt. of M.P.
- MP Biodiversity Board, Bhopal (M.P.)
- Department of Biotechnology, New Delhi
- Department of Science & Technology, New Delhi
TECHNOLOGY TRANSFER CENTRE
- A Technology Transfer Centre has been established with a view to access the scientific information of the research projects of the university in terms of innovations and/or technologies for end-users as business enterprenuers.
- It comprise of 4 Units as :
- Functional food and food safety unit
- Herbal testing unit
- Biotechnology Unit
- Panchgavya product unit

